1. Highly Sensitive Readout Detector for Si-CMOS-based Quantum Computer
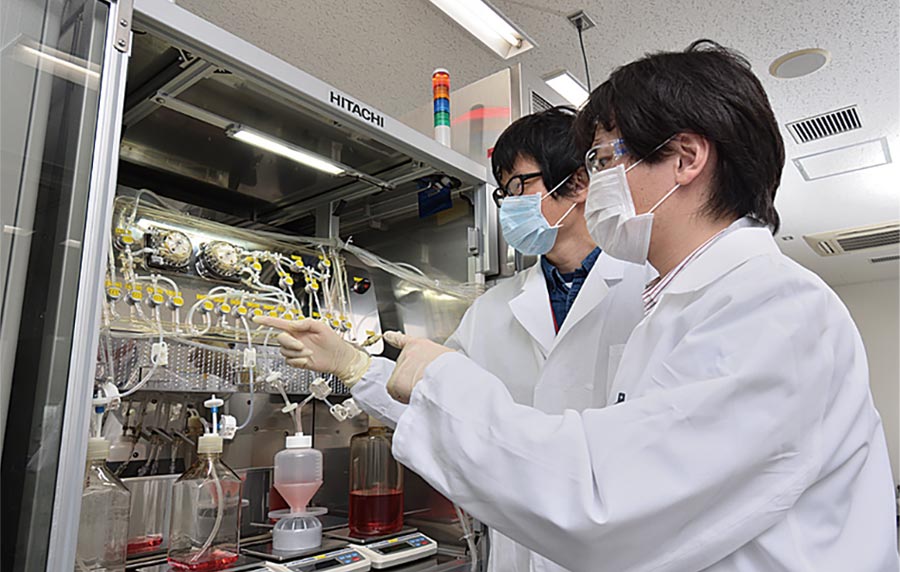
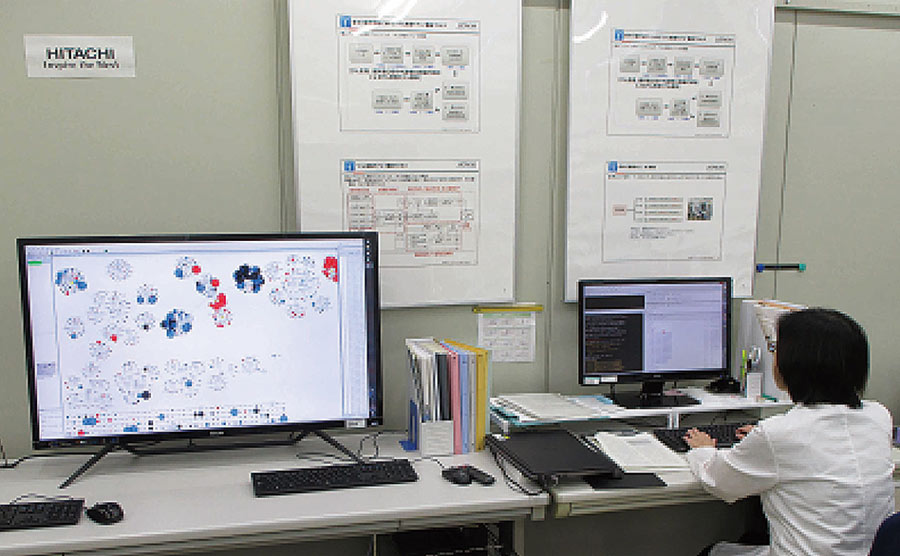
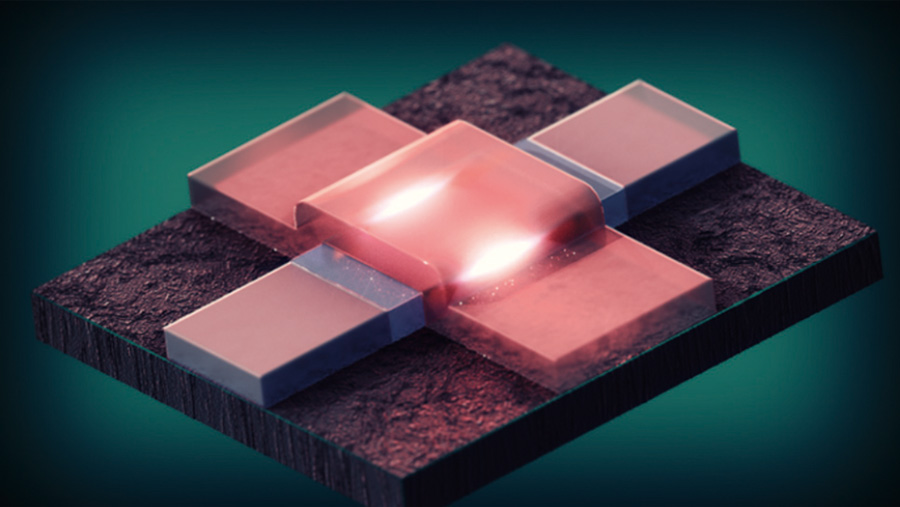
Hitachi Cambridge Laboratory has been researching quantum computing, a technology with the potential for enabling ultra-high-speed computation to help resolve societal challenges that require such complex and high-speed calculations. For reasons of future scalability and the ability to connect to existing circuits, the work has targeted quantum techniques that use silicon-based complementary metal-oxide-semiconductors (CMOS).
Joint research with University of Cambridge, University College London, and Laboratoire d'Electronique des Technologies de l'Information du Commissariat à l'énergie atomique et aux énergies alternatives (CEA-LETI) has demonstrated a readout technique with the highest ever sensitivity achieved using silicon qubits. This brings quantum computing a step closer to reality, with the charge detection sensitivity of 1.3 μe/√Hz being five times higher than any other such technique for reading silicon qubits that has been reported previously.
This research was funded by Horizon 2020, the European Union Framework Programme for Research and Innovation, (No 688539: MOS-Quito Project). It was published on July 19, 2018 in the online edition of Physical Review Applied, where it was selected as an Editor's Suggestion (recommended article).