Lumada Solution Hub for Accelerated Development and Deployment of Digital Solutions
Highlight
New companies are entering the market in a wide range of industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and finance. They are causing radical changes by using new digital technologies to create unprecedented business models. To keep pace with this environment, companies need to work rapidly on digital transformation to create new services and reform existing operations. However, this work requires a wide range of specialist technology and expertise to create business models and to build, operate, and maintain the service execution environments needed for those business models. The extensive costs and time needed are also an issue. Lumada Solution Hub is a platform provided by Hitachi that solves these issues by enabling digital solutions to be created and used more rapidly. This article provides an overview of Lumada Solution Hub and the technologies it uses.
Introduction
The use of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) has been rapidly gaining momentum in recent years, bringing major changes to the world. The rapid growth of emerging companies driven by digital technologies such as Uber Technologies Inc. and Airbnb, Inc. is resulting in destructive innovation that is radically changing the conventional structures of industries. This sudden change is creating a growing sense of crisis among a number of different industries. Companies are quickly becoming more interested in creating new services driven by digital technologies, and in digital transformation (DX) to reform their existing operations in a rapid and on-target manner(1).
Hitachi is working on Lumada projects designed to assist its customers’ DX by bringing the company’s portfolio of control/operation technology (OT) together with advanced IT applications such as big data, AI, and security. This portfolio has been accumulated through product experience in areas dealing mainly with social infrastructure. Lumada solutions are created through collaborative creation (co-creation) with customers from many different industries. A large number of customer cases have been created over the years, and the number is still growing.
Lumada Solution Hub(2), (3), (4) is a platform that helps customers grow faster by gathering together Lumada customer cases that draw on the benefits of these Hitachi OT, IT, and product assets. By promoting the use of these assets, Lumada Solution Hub enables rapid creation of digital solutions that offer high value to customers.
This article describes some problem-solving approaches that speed up the creation of digital solutions, and have been made possible by the use of Lumada Solution Hub. Some of the technologies that have emerged from these approaches are also presented.
Lumada Solution Hub for Creating Digital Solutions more Rapidly
Issues in the DX Movement
An effective approach to creating digital solutions is to isolate and correctly identify customer challenges, and then search for ideas for solving them among the pool of solution ideas in various fields that Hitachi has accumulated over the years. These ideas can then be used as a starting point for thinking of solutions. Meanwhile, the difficulty of finding applicable successful models among the accumulated pool of Lumada uses cases is currently a challenge. So an important requirement is to create a method of systematizing and running customer cases to enable instant verification.
The customer case search process sometimes yields uses cases that seem likely to meet a customer’s needs, but ultimately do not meet them completely even though the application could be executed quickly. Applications often need to be partially modified or combined with other applications, so the preparation time and effort needed to just execute a simple proof of concept (PoC) is an issue.
The heavy workload needed to operate the created service can also often become a challenge even once the PoC is finished, the working system has been safely created, and the service has started. This workload involves tasks such as operation/maintenance, contract management, billing management, and helpdesk creation.
Problem-solving Approaches Using Lumada Solution Hub
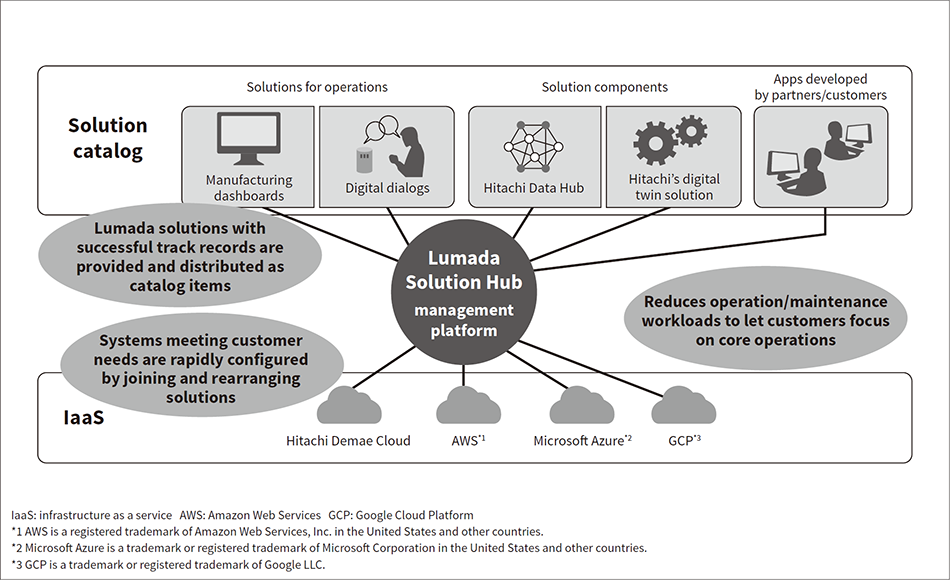
Fig. 1—Three Approaches to Solving Issues Using Lumada Solution Hub  Lumada solutions with successful track records are being cataloged, distributed, and used to promote scaling and lateral deployment.
Lumada solutions with successful track records are being cataloged, distributed, and used to promote scaling and lateral deployment.
Figure 1 shows some approaches to overcoming these challenges. The difficulty of finding applicable successful models is an issue that can be handled by registering past Lumada solutions in a solution catalog and enabling users to search it by industry, issue, or solution approach. Catalog items registered in the solution catalog provide packages of executable program code and environmental settings information so that they will run rapidly when deployed to cloud or other execution environments, enabling rapid environment creation when needed. This approach speeds up the creation of digital solutions by generating the following cycle: A Lumada solution is registered in the solution catalog along with the components it requires. The registered solution is used to create a new solution. The new solution is then registered again.
The preparation time and effort needed to just execute a simple PoC is an issue handled by providing a way to join the solutions and components registered in the solution catalog. The catalog items registered in the solution catalog are solutions with a proven track record. But since customer-specific work processes exist, these solutions may not always be transferable from one customer to another. So a mechanism is needed to enable the expertise contained in the solutions, components, and combinations within customer cases to be freely combined and re-used in block form. When data collection methods or analysis methods differ for example, this mechanism will enable their corresponding software components to be rearranged so that a system satisfying the customer’s needs can be rapidly created.
The heavy workload needed to operate the created service is an issue handled by providing managed services and business assistance services to reduce the operation/maintenance workload and let the customer focus on core operations. Workloads for IT infrastructure operation/maintenance can be reduced by providing tools and procedures as common Lumada Solution Hub services. Workloads can be reduced as long as these tools and procedures can be standardized, and even if they are not handled separately by each service provider.
Functions and Services Provided by Lumada Solution Hub
Overview of Lumada Solution Hub
Fig. 2—Overview of Lumada Solution Hub 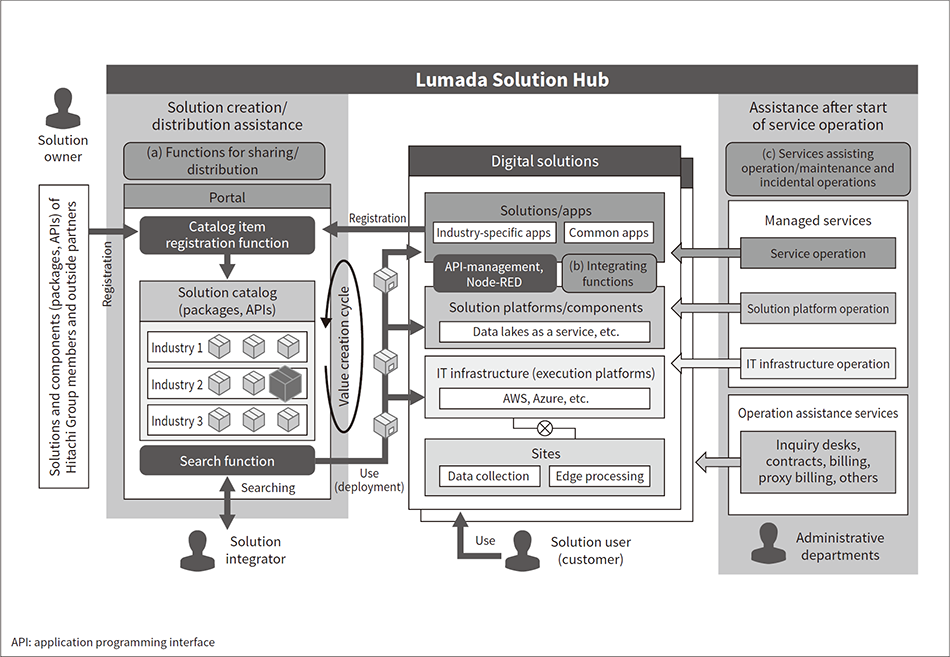 The solution owner develops and registers a solution. The solution integrator uses, builds on, and customizes that solution to release it as a cloud service to the solution user (customer). Administrative departments provide managed services and operation assistance services.
The solution owner develops and registers a solution. The solution integrator uses, builds on, and customizes that solution to release it as a cloud service to the solution user (customer). Administrative departments provide managed services and operation assistance services.
The model for providing a solution with Lumada Solution Hub is as follows: The solution owner develops and registers the solution. The solution integrator uses, builds on, and customizes that solution to provide it to the solution user (customer) in the form of a cloud service (see Figure 2).
To improve the quality and efficiency (agility and cost performance) of co-creation with the customer, the solution owner and solution integrator need a way to share and distribute knowledge and expertise about the developed solution. As shown on the left of Figure 2, Lumada Solution Hub registers solutions and components from Hitachi Group members and outside partners (solution owners) in the solution catalog as knowledge and expertise, and lets solution integrators search for items that match their objectives. Solution integrators deploy selected solutions and create environments for PoCs (see Figure 2, center). These features primarily enable Lumada Solution Hub to function as a showcase for existing Lumada solutions. The use of development tools such as Node-RED*1, (5), (12) also enables it to function as a workplace for agile development. PoC quality is improved by using Node-RED to integrate deployed solutions and components, and rearranging components or making other trial-and-error adjustments as needed.
Lumada Solution Hub helps invigorate the user value creation cycle by providing these functions to the user community (see Figure 2, left). The value creation cycle starts by extracting the re-usable parts of solutions developed through co-creation. These parts are then abstracted to enable general-purpose use, and refactored for registration and re-use as new catalog items. This loop is repeated to progressively componentize solutions. This cycle helps the process of progressively expanding and improving functions within a single project, and makes it easy to transfer the results of one project to another.
Lumada Solution Hub provides managed services and operation assistance services for new solutions created in this way. These services reduce the workloads of the solution integrator and solution owner after the service has begun operation (see Figure 2, right).
- *1
- Node-RED is a trademark or registered trademark of OpenJS Foundation in the United States and other countries.
Services and Functions Provided
Fig. 3—Portal Screen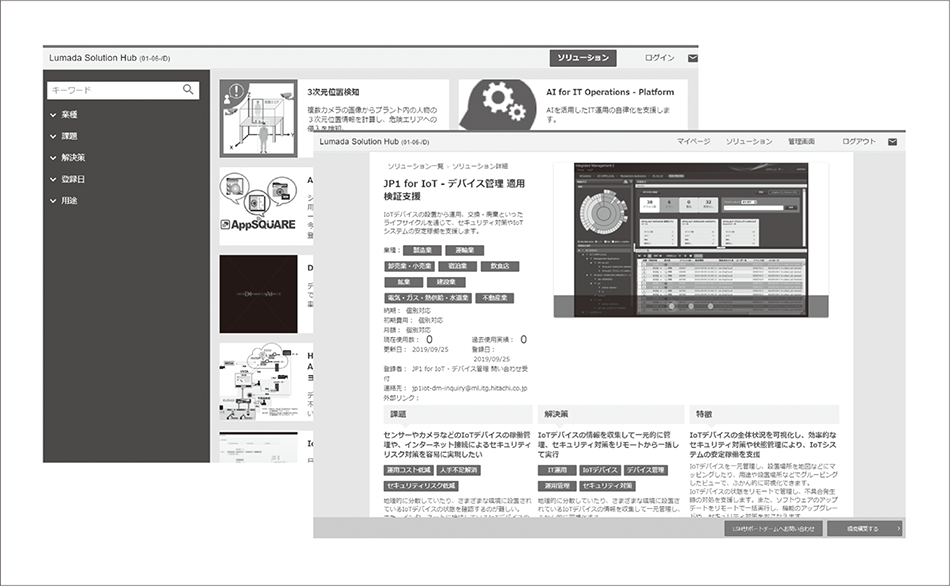 Shown here is a screen used to search for solutions or components by industry, issue, or solution approach. The screen also provides detailed descriptions of solutions.
Shown here is a screen used to search for solutions or components by industry, issue, or solution approach. The screen also provides detailed descriptions of solutions.
Fig. 4—Formats of Solutions Registered in Lumada Solution Hub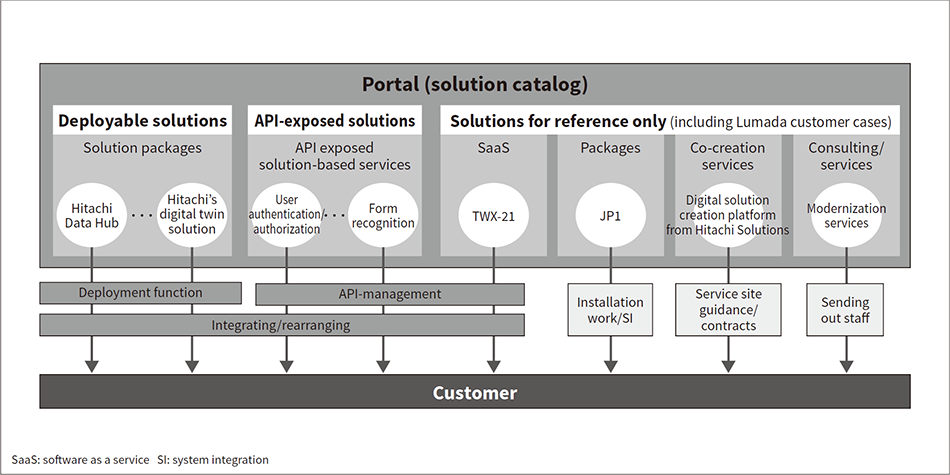 Three solution registration formats are available: (1) deployable solutions, (2) API-exposed solutions, and (3) solutions for reference only.
Three solution registration formats are available: (1) deployable solutions, (2) API-exposed solutions, and (3) solutions for reference only.
(a) Functions for sharing and distributing solutions and components
A portal function is provided as a feature to enable the solution sharing and distribution mentioned in Section 3.1. The portal enables catalog items to be registered and searched. Users can retrieve catalog items using key search information such as solution field, industry, issue, solution method, supported country/region, price, and contact information (see Figure 3). The portal also provides functions such as solution-run status checks. Solution owners can track the catalog items they own and have released by checking the solution integrators providing them, the customers they are being provided to, and their run statuses. Solution integrators can find out which catalog items are currently being re-used.
Three types of catalog items are available for registration in the solution catalog: (1) deployable solutions, (2) API exposed solutions, and (3) solutions for reference only (see Figure 4). This support for different types of catalog items enables items to be stored and used in Lumada Solution Hub in a wider range of formats.
Deployable solutions are a type of catalog item designed for applications that are deployed and used after being packaged into a format enabling execution in an infrastructure as a service (IaaS) environment. The application package formats used are Docker*2 (an industry-standard container technology)(6), Kubernetes*3 (an open-source container orchestration system)(7), and Helm*3 (an industry-standard package manager for Kubernetes)(8). Deployable solutions can run in several different infrastructure and cloud environments such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Non-containerized applications can be registered as virtual machine (VM) images, lowering the solution owner’s registration workload. Flows developed with Node-RED can also be registered to enable re-use of knowledge and expertise about solutions and component integrations.
API-exposed solutions are a type of catalog item designed for use from other applications, and for releasing application functions as APIs. The applications need to be run on a particular infrastructure or cloud, but they enable black-box use of the solution owner’s technology.
Solutions for reference only are a type of catalog item that does not fit the definitions of the other two types. This type is designed for package software and services for example, or for platform services provided by Hitachi Group members or outside partners.
- *2
- Docker is a trademark or registered trademark of Docker, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
- *3
- Kubernetes and Helm are trademarks or registered trademarks of The Linux Foundation in the United States and other countries.
Fig. 5—Example of System Development Using Node-RED 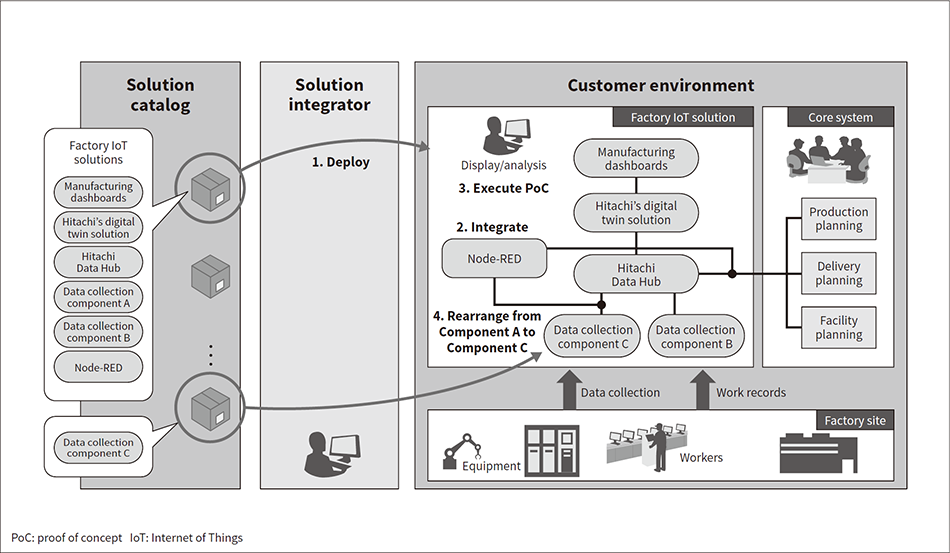 A solution registered as a solution package is selected from a list in the catalog and deployed in an environment close to the customer data. Node-RED can be used to rearrange, add, or delete tools for each component to match the types of data to be collected from the factory site.
A solution registered as a solution package is selected from a list in the catalog and deployed in an environment close to the customer data. Node-RED can be used to rearrange, add, or delete tools for each component to match the types of data to be collected from the factory site.
(b) Functions for integrating solutions and components
Lumada solutions are rooted in a system-of-systems architecture that enables access between new and existing systems(11). Solutions or components to be deployed from the solution catalog are run as microservices and connected with microservice APIs that use the Hypertext Transfer Protocol/Representational State Transfer (HTTP/REST) protocol and JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) data format. Node-RED is recommended as the function used to integrate solutions, components, or existing IT systems in Lumada Solution Hub. Node-RED is a graphical user interface (GUI)-based programming tool that lets non-IT experts develop IoT solutions that include several different services.
To execute a PoC for a factory IoT solution for example, the user starts by deploying a solution in a cloud environment after selecting it from the list of factory IoT solutions in the solution catalog. After deploying the solution, the user connects to the factory site, connects to the core system, and then executes the PoC. The user can deploy and connect another data collection component if a data collection component to be connected to Hitachi Data Hub (which handles data collection, processing, and accumulation ) needs to be changed during the PoC trial-and-error process (see Figure 5). This procedure makes solutions more re-usable by helping to reduce the differences between the solution registered in Lumada Solution Hub and the customer’s needs.
Hitachi will continue to provide functions that promote API use, including methods of registering solutions in the solution catalog and methods of authentication, authorization, and billing. These functions will be provided to enable multi-cloud environment-based integration between API-exposed solution-type services provided by Lumada Solution Hub, APIs (such as AI, IoT, and data lake APIs) provided by cloud providers, and software as a service (SaaS) offerings provided by specialist vendors.
(c) Services assisting operation/maintenance and incidental operations
Hitachi provides managed services and operation assistance services to assist operation/maintenance and incidental operations.
Managed services help customers with operation management and maintenance once the service being provided to them has begun operation. Managed services let solution integrators and solution owners check the run statuses of services created in Lumada Solution Hub’s usage environment. They monitor resources, performance, and event logs, and provide security measures and regular statistical reports on operations. They also provide access control, virus scans, intrusion detection, and software vulnerability information, along with security updates and other security assistance. While most of the services currently available are for the IT infrastructure layer, Hitachi is planning to progressively augment the service lineup to provide functions such as operation/maintenance of higher-level solution platforms and proxy operation of entire services.
Operation assistance services are services that assist with common (mostly business-related) operations done once the solution is being provided, such as inquiry desk operations, contract operations, and billing/proxy billing operations. Hitachi is planning to provide these services by drawing on the expertise gained from the TWX-21 SaaS business platform service(10) it currently provides.
Conclusions
This article has provided an overview of Lumada Solution Hub, a platform that helps customers grow faster by rapidly creating digital solutions that provide them with high value. Some functions and services emerging from this platform have also been presented.
DX activities designed to enable rapid and on-target creation of new services, operation reforms, or other innovations driven by digital technologies will continue to gain momentum in the years ahead. So platforms assisting these activities will play an increasingly important role. Hitachi is a DX innovation partner that will continue to pursue co-creation activities with customers around the world, focusing on the project domains of Mobility, Smart Life, Industry, Energy, and IT. The company is looking forward to having Hitachi Group members and outside partners use Lumada Solution Hub by serving as solution owners and solution integrators. Hitachi wants to bring new value to customer projects and the world at large by creating and invigorating a Lumada Solution Hub community and ecosystem.
REFERENCES
- 1)
- Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), “Report on Digital Transformation (DX) –Overcoming of ‘2025 Digital Cliff’ Involving IT Systems and Full-Fledged Development of Efforts for DX– (Summary)” (Sep. 2018) (PDF Format, 60.4kB)
- 2)
- Hitachi News Release, “Hitachi Launches ‘Lumada Solution Hub’ to Advance and Facilitate Introduction of Lumada Solutions,” (Mar. 2019)
- 3)
- H. Nakamura et al., “Lumada Platform Services for Creating New Value,” Hitachi Review, 68, pp. 526–531 (Sep. 2019).
- 4)
- “Lumada Platform Service: Lumada Solution Hub,” Hitachi Review, 69, pp. 273–274 (Mar. 2020)
- 5)
- Node-RED, “Low-code programming for event-driven applications,”
- 6)
- Docker
- 7)
- Kubernetes
- 8)
- Helm
- 9)
- Hitachi, Ltd., “Data Collection, Processing, and Storage Solution ‘Hitachi Data Hub’” in Japanese
- 10)
- TWX-21
- 11)
- M. Iwasaki et al., “Lumada’s Digital Innovation Platform Supporting Sustainable Development and Operation of Infrastructure Systems,” Hitachi Review, 69, pp. 621–626 (Sep. 2020).
- 12)
- H. Nishiyama et al., “Hitachi’s Use of Node-RED for Rapid Solution Development and Associated OSS Activities,” Hitachi Review, 69, pp. 634–638 (Sep. 2020).








